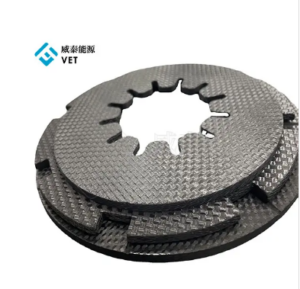
A GRAPHITE SUSCEPTOR delivers precise, even heating during chip production. This component holds heat well and keeps temperature stable. Engineers trust the GRAPHITE SUSCEPTOR to create chips with high quality and reliability. Uniform heating supports advanced manufacturing and helps prevent defects.
Key Takeaways
- Graphite susceptors provide even and stable heating, which helps produce high-quality chips with fewer defects.
- Graphite’s unique properties, like heat resistance and chemical stability, make it ideal for precise chip manufacturing.
- New coatings and materials improve graphite susceptors’ durability, boosting chip production efficiency and reliability.
GRAPHITE SUSCEPTOR: What It Is and How It Works
Definition and Core Function in Chip Manufacturing
A GRAPHITE SUSCEPTOR acts as a specialized component in chip manufacturing equipment. Engineers design it to absorb electromagnetic energy and convert it into heat. This heat then transfers directly to the wafer or substrate, ensuring a stable and uniform temperature during processing. The GRAPHITE SUSCEPTOR sits inside reactors or furnaces, holding the wafer in place while controlling the thermal environment.
Manufacturers rely on this component for several reasons:
- It delivers consistent heating across the entire wafer surface.
- It resists chemical reactions, even at high temperatures.
- It maintains its shape and strength during repeated heating cycles.
Note: Consistent temperature control helps prevent defects and improves chip yield.
Role in Semiconductor and Epitaxy Processes
The GRAPHITE SUSCEPTOR plays a vital role in both semiconductor fabrication and epitaxy. In semiconductor processes, it supports the wafer during steps like chemical vapor deposition (CVD) and rapid thermal processing (RTP). These steps require precise temperature management to grow thin films or layers on the wafer.
In epitaxy, the susceptor ensures that each atomic layer forms evenly. Uniform heating allows atoms to arrange themselves in the correct pattern, which is essential for high-performance chips. The susceptor’s thermal stability also reduces the risk of hot spots or cold zones, which can cause uneven growth or defects.
| Process Step | Susceptor Function | Benefit to Chips |
|---|---|---|
| CVD | Provides uniform heating | Smooth, defect-free films |
| RTP | Rapid, controlled temperature rise | Faster, reliable results |
| Epitaxy | Maintains atomic-level precision | High-quality crystal growth |
Engineers continue to improve susceptor design to meet the demands of advanced chip technology. The GRAPHITE SUSCEPTOR remains a cornerstone of modern semiconductor manufacturing.
GRAPHITE SUSCEPTOR: Precision, Benefits, and Innovations
Why Graphite Is Chosen—Material Properties and Advantages
Engineers select graphite for susceptors because of its unique properties. Graphite handles high temperatures without melting or warping. It resists chemical attacks from gases used in chip manufacturing. The material also conducts heat evenly, which helps keep the wafer at a steady temperature.
Key advantages include:
- High thermal stability
- Low risk of contamination
- Strong resistance to thermal shock
Tip: Graphite’s low thermal expansion means it keeps its shape even after many heating cycles.
Impact on Process Control, Yield, and Chip Quality
A GRAPHITE SUSCEPTOR gives engineers tight control over the heating process. This control leads to better chip quality and higher yields. Uniform heating prevents hot spots and cold zones, which can cause defects.
A simple table shows the benefits:
| Benefit | Result for Chip Production |
|---|---|
| Even temperature | Fewer defects |
| Stable environment | Consistent chip performance |
| Fast heat response | Shorter production times |
Manufacturers trust the GRAPHITE SUSCEPTOR to deliver reliable results batch after batch.
Challenges and Recent Advances in Susceptor Technology
Despite its strengths, graphite faces some challenges. It can oxidize at very high temperatures if exposed to air. Engineers now use coatings to protect the susceptor surface. Recent advances include new graphite grades and improved surface treatments. These innovations help extend the life of the susceptor and boost chip quality.
Note: Ongoing research continues to make susceptors more durable and efficient.
- The GRAPHITE SUSCEPTOR stands as a vital tool in chip manufacturing.
- Its unique features help engineers achieve precise results and high-quality chips.
- Ongoing improvements in this technology support better performance and efficiency in the semiconductor industry.
FAQ
What makes graphite ideal for susceptors?
Graphite handles high temperatures and resists chemical damage. It keeps its shape during heating cycles.
Engineers value its stability and reliability.
How do engineers protect graphite susceptors from oxidation?
They apply special coatings to the surface. These coatings block oxygen and extend the susceptor’s life.
- Common coatings include silicon carbide and other ceramics.
Can graphite susceptors be reused in chip manufacturing?
Yes, manufacturers reuse graphite susceptors for many cycles.
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Durability | Cost savings |
| Stability | Consistent use |